No matter how much work you do to create high-quality, targeted content, there are still plenty of troubling technical SEO pain points that can sabotage your success when it comes to ranking high in search results and delivering the kind of optimum user experiences that help your site grow.
In this guide, we outline 9 of the most common technical SEO issues, their impact on your website, and, most importantly, what to do about them.
9 Technical SEO Pain Points And What to Do About Them
1. Unindexed Pages
Indexing is a process through which search engines such as Google access, analyze, and ultimately store web pages in their enormous search database, commonly known as an “index.”
If crawlers determine that the page is valuable and relevant for users, it gets stored in the index, giving it the potential to appear in search results for relevant queries.
The Problem:
If your pages aren’t in its index, Google has no way of knowing they exist.
Thus, they won’t appear in search results, Won’t drive any organic search traffic to your website, and will have minimal -if any- impact on your ability to generate conversions.
The Cause:
There are several reasons why your pages aren’t being indexed. These include:
A. Your Site is New
If your site hasn’t been live for very long, search crawlers may not know about it yet, especially if it doesn’t have any incoming links pointing to it.
B. Canonicalization Issues
A common technical SEO problem for eCommerce stores is that canonicalization issues occur when two pages have identical or nearly identical content, meaning Google doesn’t know which one to index.
C. Broken Links and Site Errors
Broken links act as dead ends, preventing crawlers from accessing valuable content, while site errors such as slow loading times or server crashes can altogether exclude pages from being indexed.
The Solution:
To address problems with your pages not being indexed on Google:
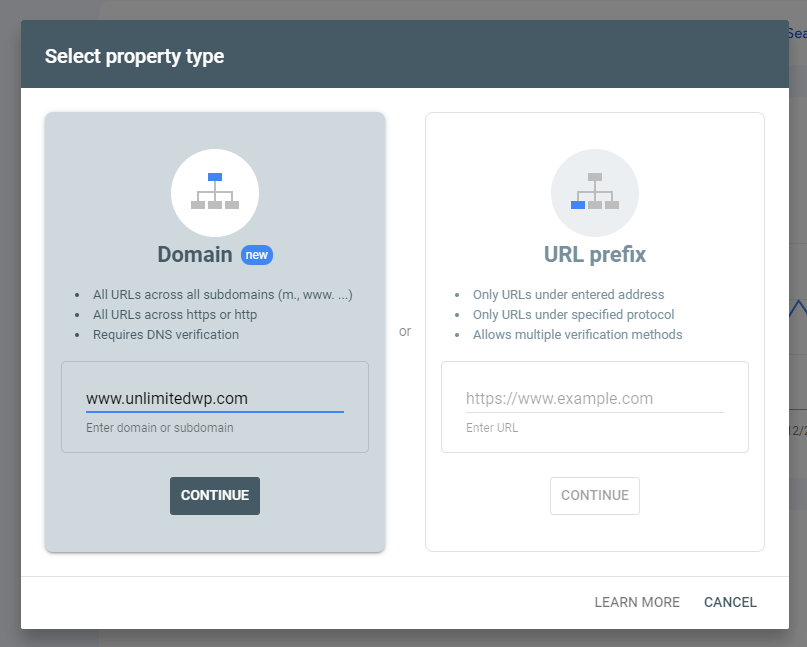
A. Submit Your Site to Google Search Console
If you haven’t already set up a Google Search Console account for your website, we recommend you stop what you’re doing and go do that right now.
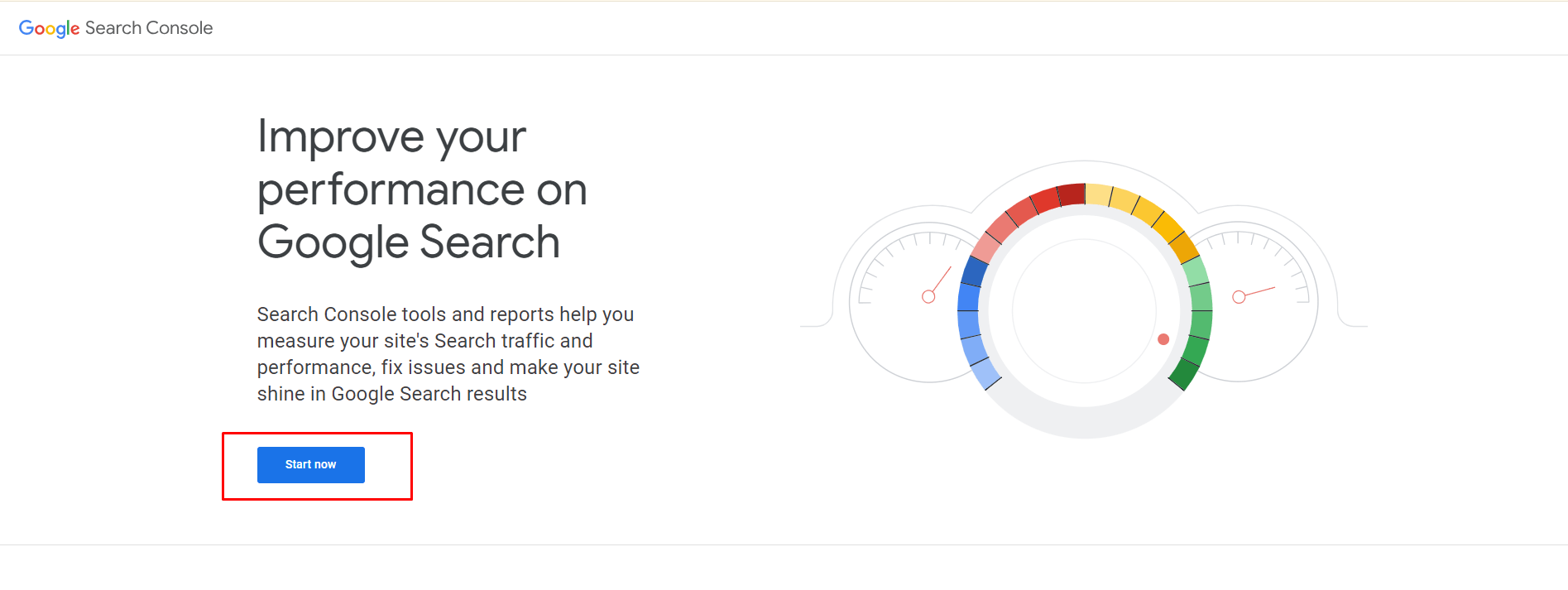
After signing in with your existing Google account, you can add your domain to connect it to Search Console.
Finally, you’ll be asked to verify your website, after which your account will be almost ready.
B. Check Search Console for Indexing Issues
Once Search Console has gathered your data, you can go to Indexing – Pages to get an overview of the number of pages that have and haven’t been indexed.
PRO TIP: The goal here isn’t to have 100% of your URLs indexed. The only ones you need to worry about are the canonical URLs. You can think of these as the “official URLs” for your content.
For example, you might have the same information across multiple URLs, like product pages accessible through different categories. In this case, you would only need to ensure that the main product page is marked as canonical and indexed.
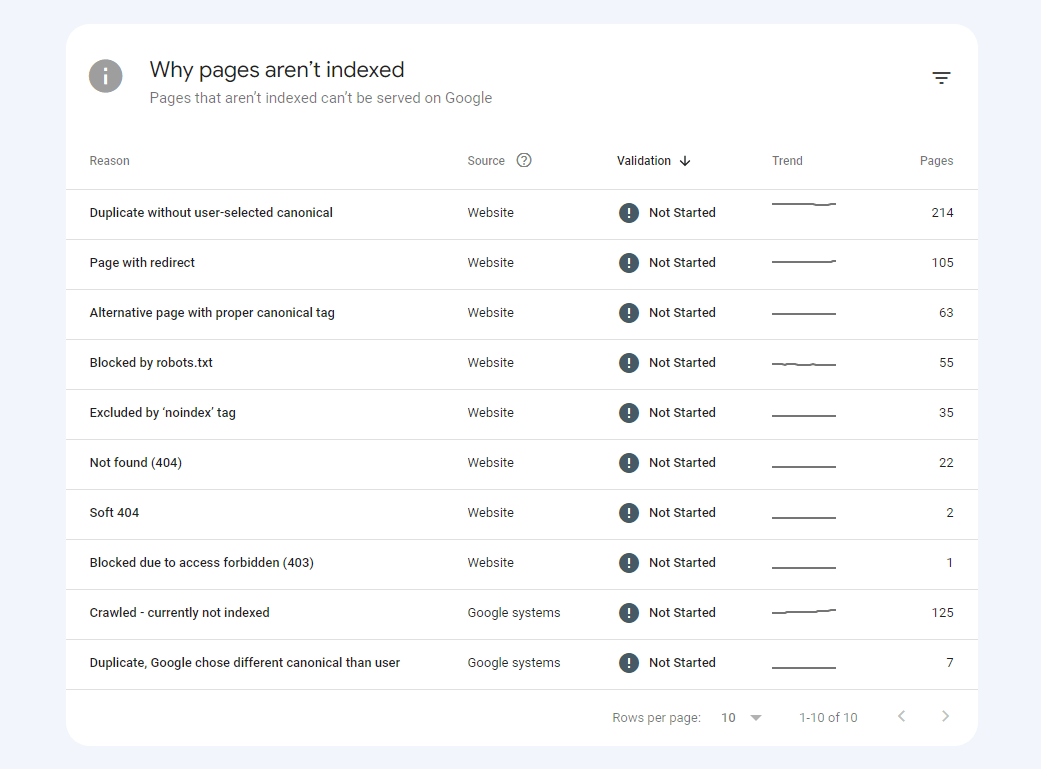
If there are pages that are not in Google’s index, you can scroll down to find out why.
Here, you’ll get a list of all the technical issues that are preventing your pages from being indexed.
From there, you can click on any of the reasons to get a full list of the URLs it affects.
With that done, you can refer to Google’s index troubleshooting guide to identify the right course of action to take.
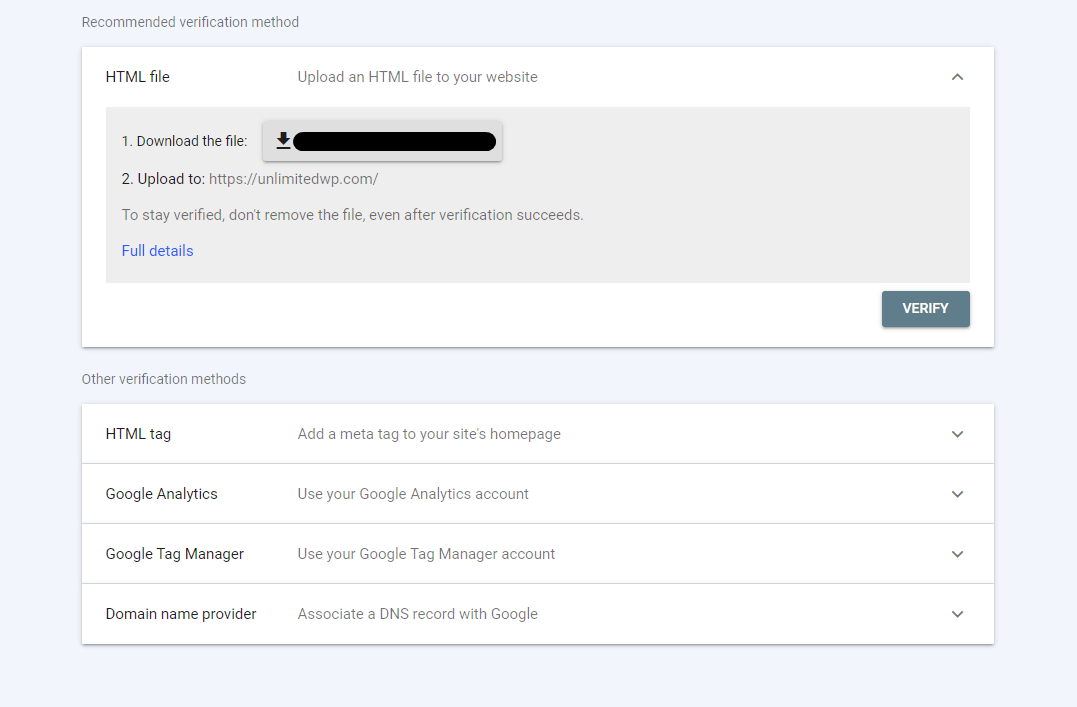
C. Request Indexing
When you’ve finished fixing each non-indexed page, you can submit its URL to the URL Inspection tool and request that it be indexed.
PRO TIP: Search crawlers sometimes take a while to go through your site. You can speed things up by using the URL inspection tool to manually submit URLs for each new piece of content, as shown in Step C above.
2. Robots.Txt Errors
Robots.txt is a simple yet powerful file that tells search engine crawlers which pages they should access and which they should ignore.
The Problem:
A misconfigured robots.txt file can result in a number of indexing problems:
- Unindexed Pages – Pages that you want to be indexed aren’t because the Robots file tells search crawlers to ignore them, meaning that content won’t appear in search results.
- Accidental Indexing – Pages you don’t want indexing (like your WordPress login page, for example) end up appearing in search results there because you didn’t disallow them in Robots.txt, posing a threat to website security and potentially leading to poor user experiences.
The Cause:
Most Robots.txt problems are caused by simple human error, such as a basic typo or an overlooked URL that shouldn’t be there.
It could also be because your file is outdated. If you’ve made significant changes to your website and its structure, or if your goals and objectives have changed, it pays to utilize the following solution to check your file is still accurate.
The Solution:
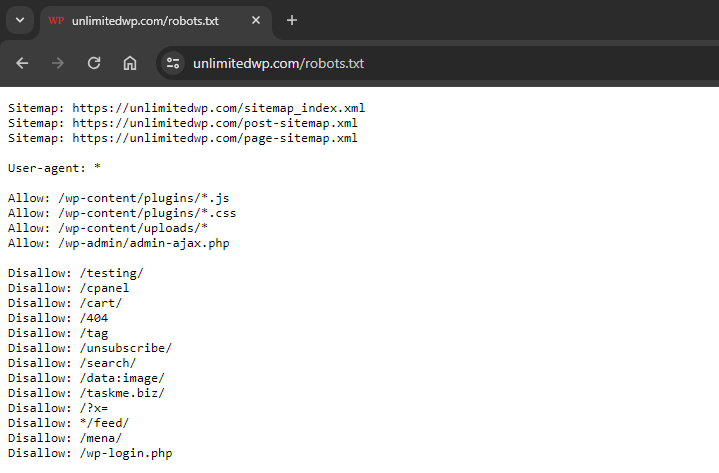
First, access your Robots.txt file. This is typically found in the root directory of your site; you can access it simply by adding robots.txt to the end of your domain name like this:
https://unlimitedwp.com/robots.txt
Next, look at anything that has Allow next to it. That tells search crawlers they’re allowed to crawl and index that page or resource.
If anything shouldn’t be there, log into your hosting server, download the Robots.txt file, and remove it.
From there, look at the Disallow list, which shows you all the URLs that search bots are blocked from crawling. Are there any URLs in that list that should be indexed but are currently blocked?
If so, simply edit the file and remove it.
Finally, add any custom Allow or Disallow rules you want to add, save your file and re-upload it to your server.
You should now find that search crawlers have a better understanding of which pages to crawl and which to ignore, which will go a long way to improving your indexability, security, and user experience.
Pro Tip: Check out How to Optimize Robots.Txt to discover more ways to make the most of this valuable file.
3. Manual Actions
Manual actions are the official term for the dreaded “Google Penalties” that so many website owners and SEO pros fear.
The Problem:
A manual action essentially serves as a red flag held up against your site by Google’s human search reviewers when they determine that your site goes against the company’s guidelines.
At best, a manual action can cause your website’s search rankings to plummet, resulting in a significant loss of organic traffic.
At best, they can result in your site, or at least some of its pages, being de-indexed, meaning they won’t appear in search results at all.
The Cause:
A manual action is usually taken against pages that use black hat SEO strategies in an attempt to manipulate ranking algorithms, typically resulting in a poor user experience.
- Unnatural links – Buying links, engaging in link schemes, or having low-quality backlinks pointing to your site.
- Cloaking & redirects – Deceiving users or search engines by showing content different from what’s indexed.
- Keyword stuffing – Overusing keywords unnaturally in your content to manipulate rankings.
- Hidden content – Text or links hidden from users but visible to search engines.
- Thin content – Pages with low value or insufficient unique content.
- Spammy content – Stuffing pages with irrelevant keywords, deceptive content, or blatant plagiarism.
The Solution:
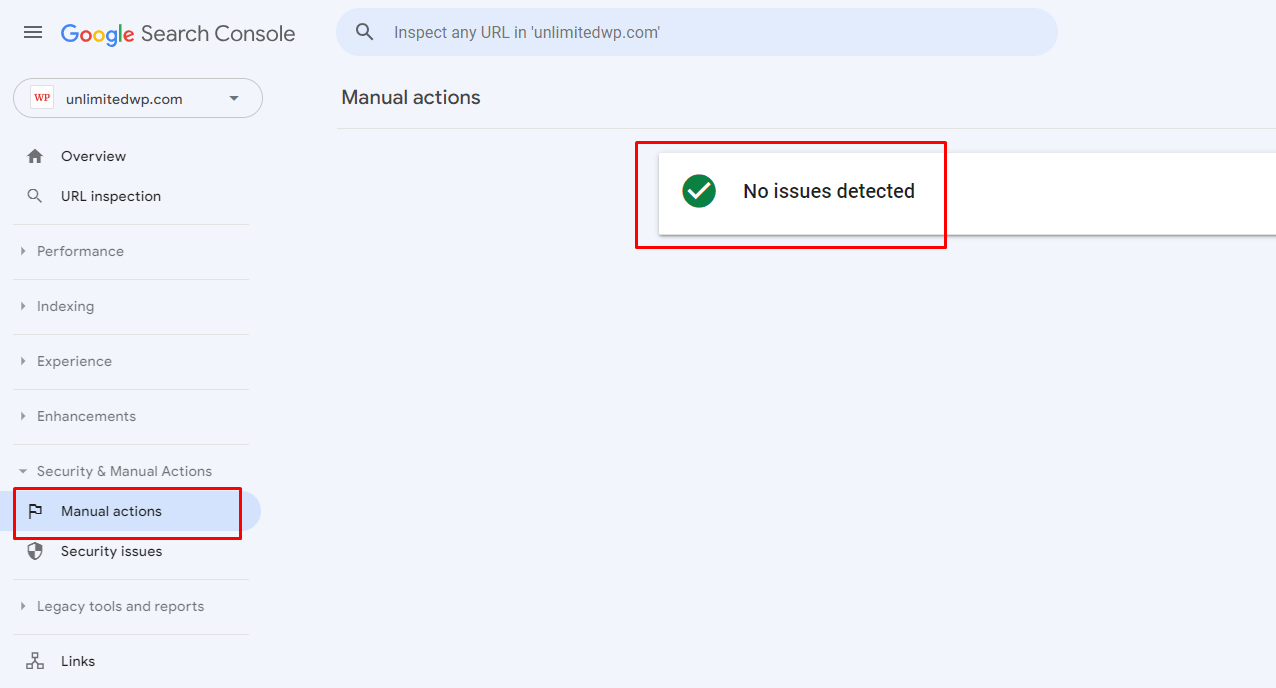
You can check if you have any manual actions against your site via Google Search Console.
Log in and navigate to Security & Manual Actions – Manual Actions.
Ideally, you’ll see a page like the one above, which displays a “no issues detected” notification, meaning you’re in the clear.
Otherwise, this is where you’ll see any actions you need to address, along with links to useful guidance from Google outlining how to correct the issue.
4. Unsecure Site Connection
Few technical SEO problems have the potential to cause more havoc than an unsecured connection.
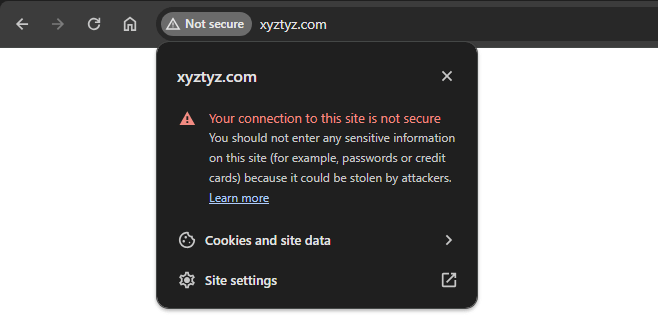
You’ll know that your site isn’t properly secure when the padlock symbol that normally appears next to a website address in your browser is missing.
Usually, it’s replaced with a “not secure” warning, advising users to be wary of trusting your site with sensitive personal information.
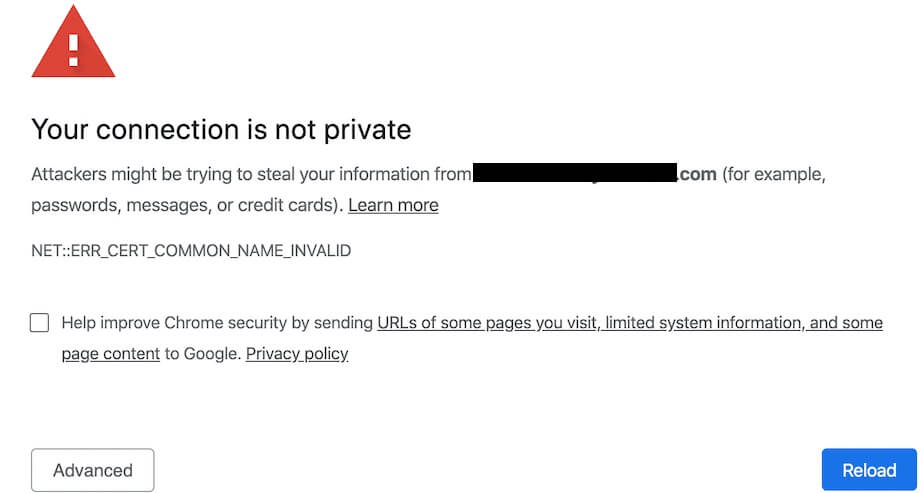
It may also result in a “your connection is not private” error like the one above, which can stop users from ever getting to your site in the first place.
The Problem:
Running your site without a secure, encrypted connection leaves you vulnerable to:
- Data breaches – Sensitive information like login credentials, financial details, and user data are more susceptible to theft by malicious actors on the network.
Did You Know? Gartner predicts a 45% increase in cyber attacks by 2025, making a secure site more important than ever.
- SEO penalties – Search engines prioritize secure websites, relegating unsecured ones to lower search rankings, impacting website visibility.
When you think about it, this makes sense:
95% of websites ranked on Google are properly encrypted. So why should the search giant place your site high in search results when there are countless, more secure ones available?
Loss of Trust and Customer Confidence – In an age when cybersecurity awareness is at an all-time high, stumbling across an unsecured connection can raise some major alarm bells, leading to abandoned visits and lost conversions.
The Cause:
The most common culprit behind an unsecured website is the absence of an SSL certificate, which encrypts communication and verifies your site’s identity.
The Solution:
Since the main cause of an unsecured website is a lack of SSL certificate, the solution, of course, is to get one and install it.
In many cases, you’ll find that your hosting and/or domain provider also sell SSL certificates and will provide clear instructions on how to install and activate them.
If that’s not the case, you can get an affordable certificate from companies like SSL.com.
You could also use a WordPress plugin like WP Encryption, which sets you up with a free SSL certificate via Let’s Encrypt.
Pro Tip: Convinced your site is encrypted but still having problems? Read WordPress Can’t See My SSL Certificates: What Should I Do? to find the solution.
5. Slow Loading Times
In the online world, the time it takes your pages to load can mean all the difference between success and failure.
Pages that take too long to load can be a major turn-off to users, while those that fire up as quickly as possible deliver the kind of positive user experience that can result in more conversions.
Did You Know?
Conversion rates are three times higher for eCommerce websites that load in under a second.
The Problem:
Slow page speeds harm both user experiences and your WordPress SEO optimization efforts.
No matter what lengths you go to target keywords with high-quality content, and no matter how many other technical SEO best practices you adhere to, underperforming pages will increase your bounce rate and send negative signals to Google, resulting in reduced search visibility.
The Cause:
Several factors can conspire to slow down your website:
- Uncompressed Content – Large image, video, and script files that haven’t been optimized require more resources to load in a browser, slowing down page speeds.
- Lack of Server Resources – It may be that you’re on an overcrowded shared hosting server, with other sites using up more than their fair share of resources. Alternatively, it may be that your site has simply outgrown your hosting plan, and you’re getting more traffic than your server can handle.
- Poor Quality Code – Inefficient, unoptimized code takes longer for browsers to read, negatively affecting your site performance.
The Solution:
There are so many ways to improve page speeds that we had to create a separate guide to WordPress speed optimization just to cover them all.
If you don’t have time to read all that right now, here’s how to get a few quick and easy wins.
- Optimize Your Media Files – Use top WordPress image optimization plugins like Smush to compress your files, reducing their burden on your server.
- Upgrade Your Web Hosting – If it’s your hosting server that’s the problem, you may want to choose a better plan or pick a new web hosting provider.
- Use SEO-Optimized Themes and Plugins – Make sure that any WordPress themes or plugins that run on your site are designed with clean, minimalist, lightweight code to ensure better performance.
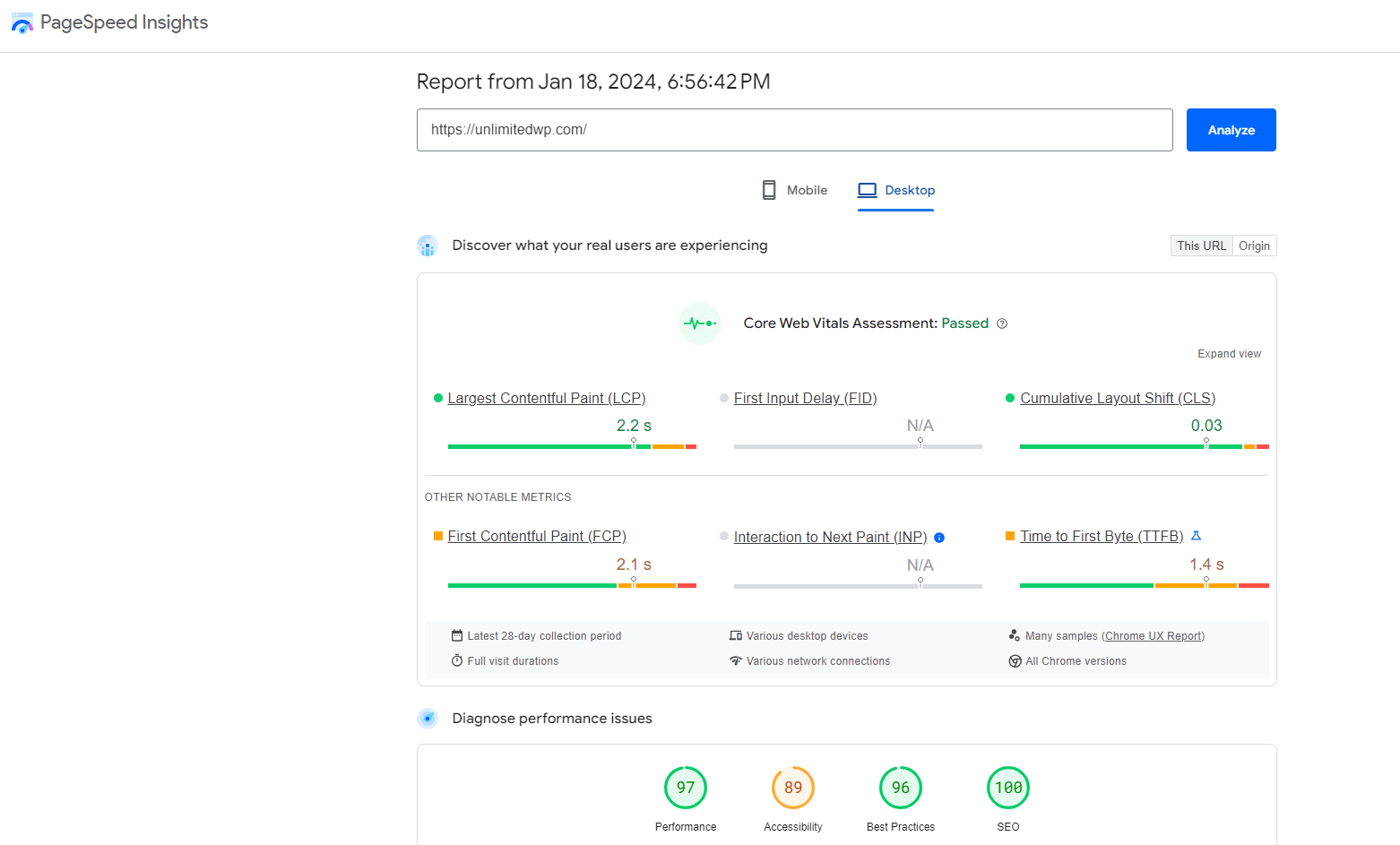
PRO TIP: Use the free Google Page Speed Insights tool to test your page load speeds and identify areas for improvement.
Remember to test on both mobile and desktop to ensure users get the best experience no matter which device they use.
6. Poor Mobile User Experiences
57.8% of all global Internet traffic comes from mobile devices. To put that into perspective, that’s roughly 17% more than the amount of traffic generated by desktop users.
So you can see why making your website mobile-friendly is one of the most crucial technical SEO best practices to follow.
The Problem:
Pages that are not designed with mobile devices in mind can cause major usability problems.
Whether it’s the text, that’s too small to read, buttons crammed so close together that users accidentally click on the wrong one, or malfunctioning layouts that require unintuitive horizontal scrolling to see all your content, mobile optimization issues are the kind of problem that few users have the patience for.
They’ll simply abandon your site in frustration, something which Google perceives as a sign of a poor user experience and demotes your content in search results as a result.
The Cause:
Though a wide range of things could be responsible for poor mobile experiences, the usual suspects include:
- Non-Responsive WordPress Themes – Themes built without prioritizing mobile responsiveness leave users struggling to view and engage with your content.
- Overlooking Interactive Elements – Buttons and links that are designed only with mouse clicks in mind can be too small and close together to be properly clicked with the human thumb, leading to accidental taps and annoyed users.
- Overly Large Images – Remember what we said about oversized, unoptimized images slowing down your site performance? That’s as true on tablets and smartphones as it is on desktop devices.
The Solution:
Use the Develop tools available in the Chrome and Firefox web browsers to test how your site displays and functions on different devices and screenshots.
You can access these tools by right-clicking anywhere on your website and choosing Inspect.
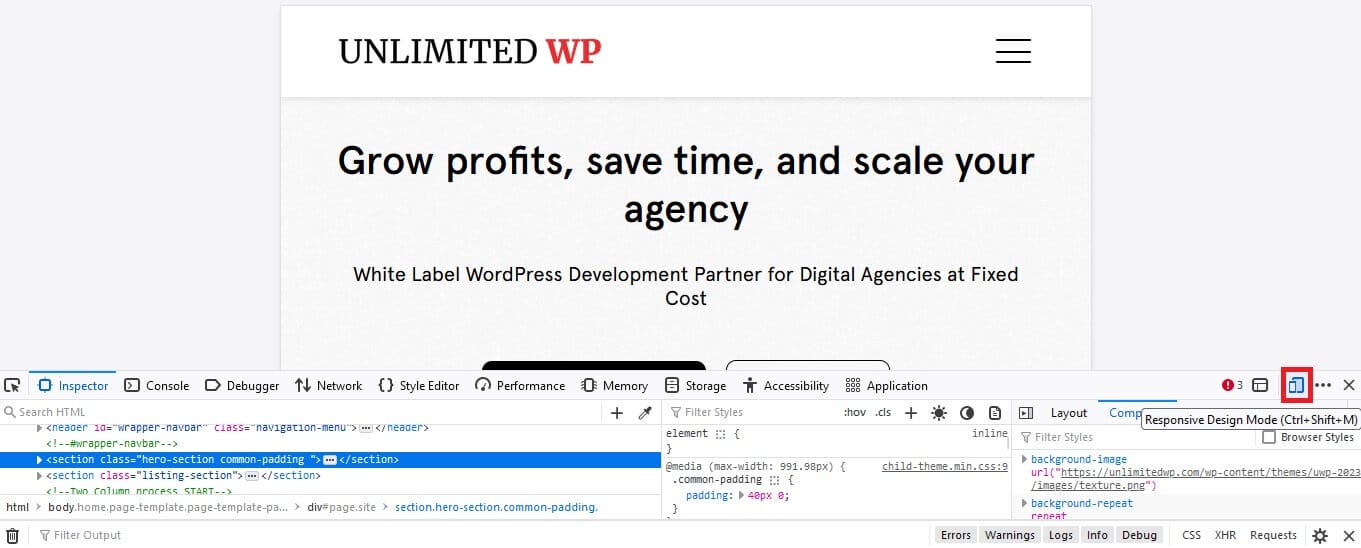
Next, click on the device icon to access responsive design mode.
Here’s what that looks like in Firefox:
And here’s the same thing in Google Chrome:
From there, you can use the drop-down menu to explore how your site performs on a range of popular mobile devices.
Look for the issues listed above, along with anything else that you think might be detrimental to your site’s mobile-friendliness.
Wherever possible, you’ll also benefit from testing your site on as many different physical devices as you can, looking out for any problems with your interactive elements and navigation.
Once you’ve identified any known problems, it’s time to either open your site editor and fix them or swap to a new, more mobile-friendly WordPress theme.
7. Missing Sitemaps
A sitemap is an organized list of all the URLs on your website, which serves as a kind of roadmap to help search engines discover and index your content.
Along with some of the other technical SEO best practices listed in this guide, they can prove invaluable for ensuring your content shows up for the right search terms.
The Problem:
A missing, misconfigured, or error-ridden sitemap means that search crawlers have limited information about your content and how pages relate to one another, meaning valuable pages remain undiscovered and unindexed.
The Cause:
The three leading causes of sitemap problems include:
- Not submitting a sitemap in the first place – It may be that you simply forgot to create and submit a sitemap. Of course, if you’ve never heard of them until now, you likely didn’t even realize you had to.
- Formatting Errors – Faulty syntax or structure can render your sitemap incomprehensible to search engine crawlers.
- Website Updates and Upgrades – If you’ve recently revamped your website with a new content structure, perhaps even added and removed lots of pages, there’s a good chance that your sitemap is simply out of date.
The Solution:
Here’s a simple strategy to solve the most common sitemap errors:
A. Check Your Sitemap Exists
The first task is to check that a sitemap exists in the first place.
Like Robots.txt, this file is normally located in your root directory, so you can access it by typing the file name after your URL like so:
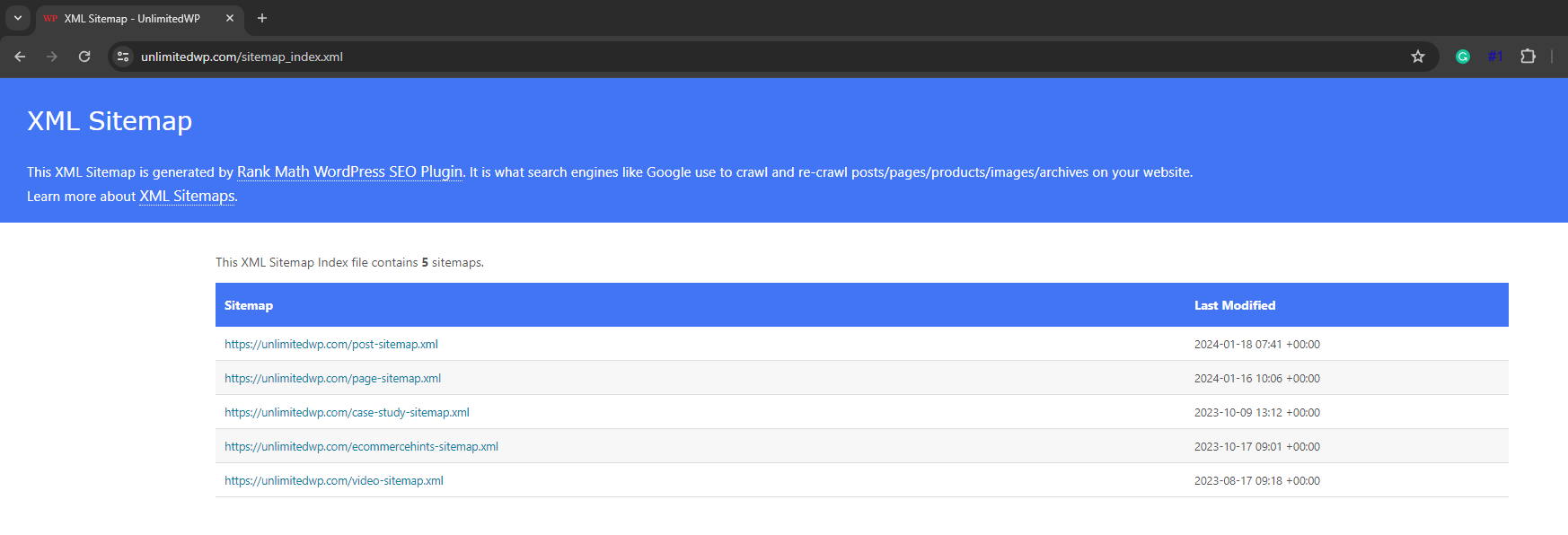
yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
or:
https://unlimitedwp.com/sitemap_index.xml
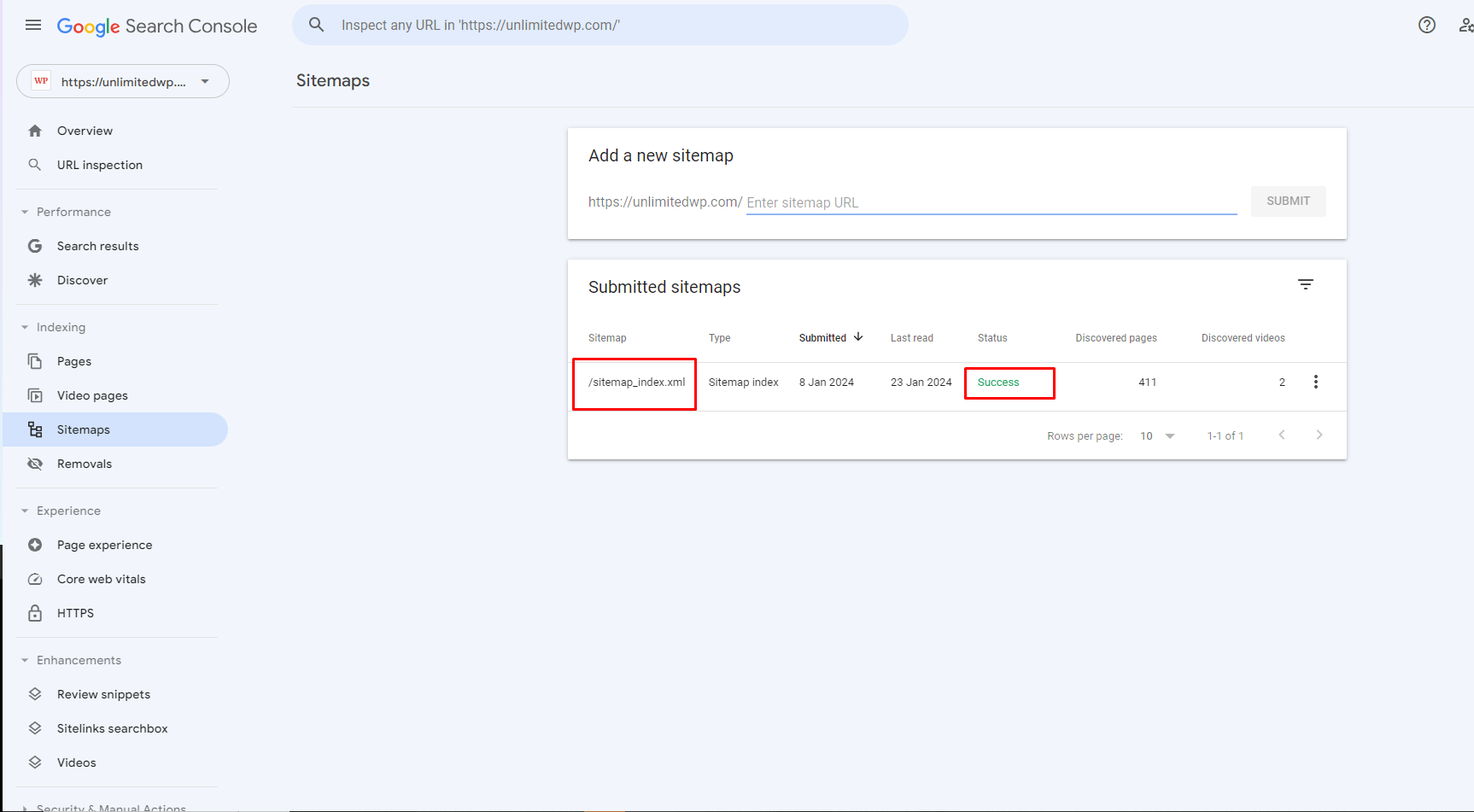
If your sitemap has already been submitted to and crawled by Google, you can also find its location by going to – Indexing – Sitemaps.
B. Create A New Sitemap if Necessary
You can automatically generate an XML sitemap for your website using SEO optimization plugins like Rankmath SEO.
See How to Create a Sitemap for easy-to-follow instructions.
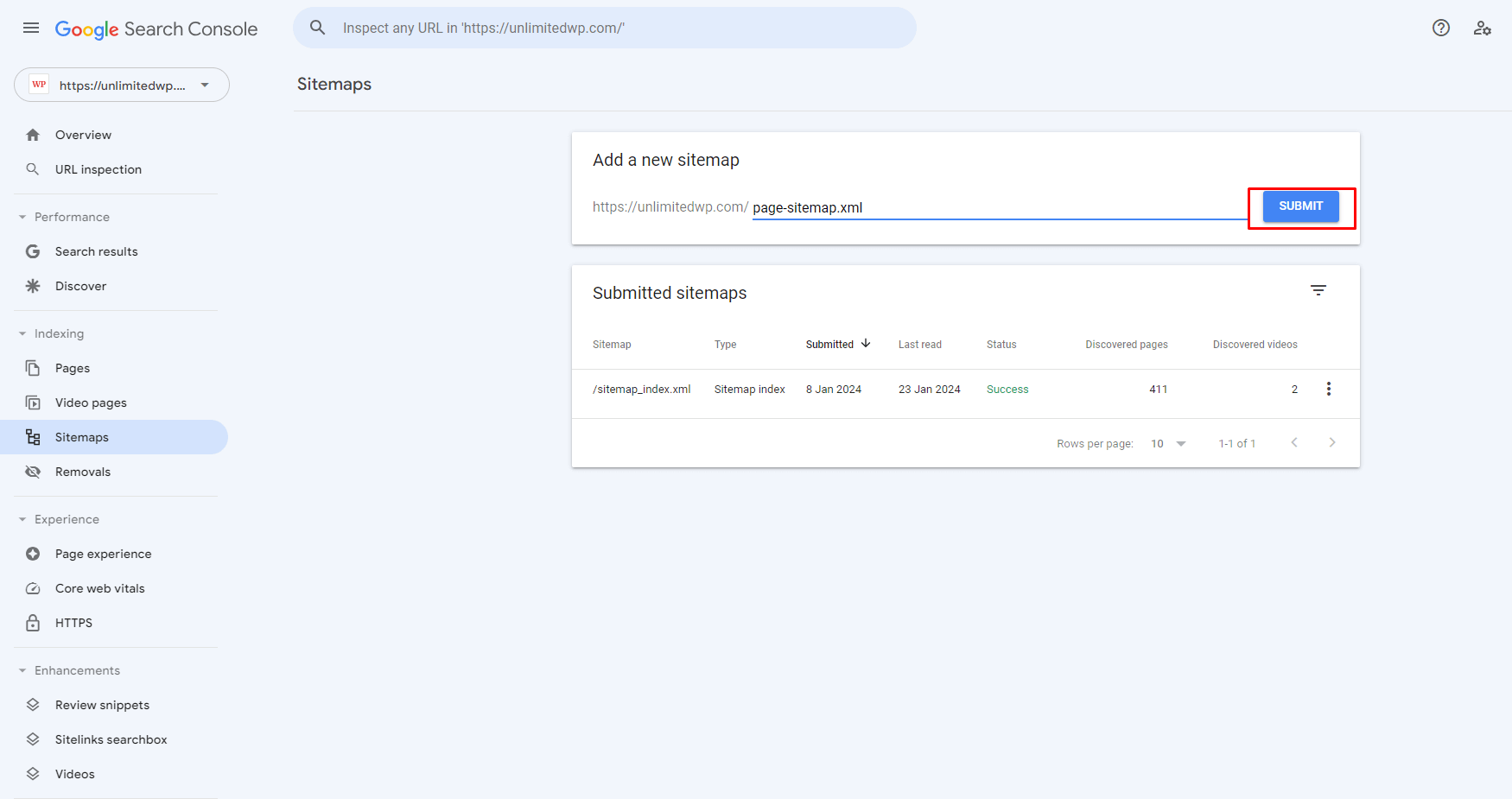
C. Submit Your Sitemap
After creating your sitemap, go to the aforementioned Sitemaps page on the Search console, add its URL into the box provided, and click submit.
D. Check Your Sitemap for Errors and Resubmit if Needed
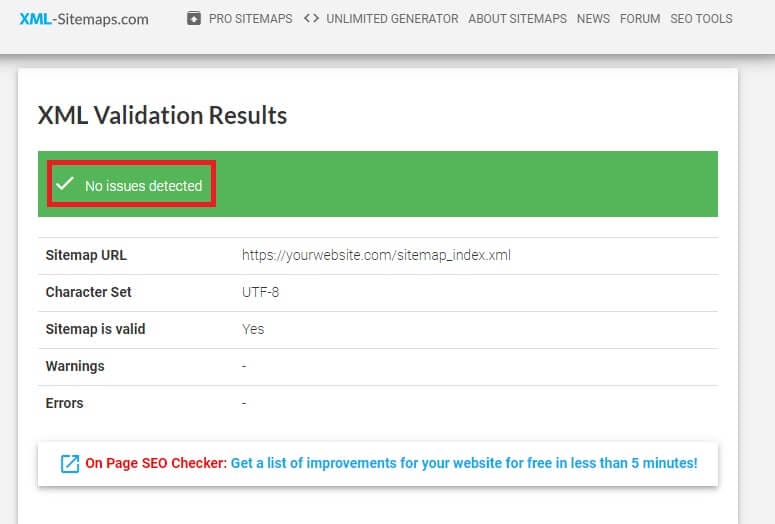
Finally, you can test your sitemap for potential problems using a free XML validator.
This will reveal any known problems and provide guidance on how to fix them.
8. Broken Links
Broken links are any hyperlinks on your website that point to a page or resource that isn’t there. This applies to both internal and external links.
The Problem:
The impact of broken links on user experience and search visibility can be significant.
If you’ve ever clicked on a link and it’s taken you to the wrong page or a page with a 404 error, you’ll know how frustrating it can be. When users can’t find the resource they’re looking for, not only are you not generating any leads, sales, or ad clicks, but you’re also giving those users a good reason to leave your site altogether, meaning higher bounce rates.
What’s more, when search crawlers follow a broken link, they hit a dead end, meaning valuable content may not be indexed because it can’t be found.
The Cause:
As websites evolve, pages tend to get moved around, redirected, or removed altogether. When this happens, its URL changes, which means that any links that originally pointed to that page will no longer work.
The Solution:
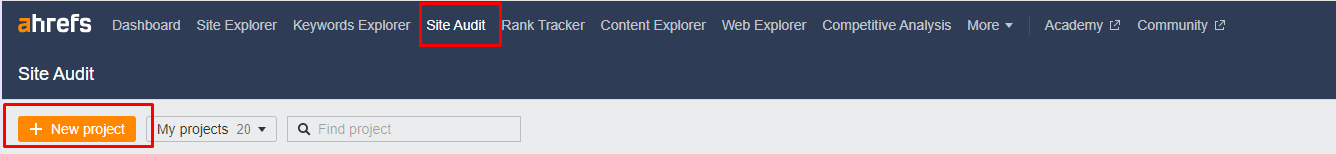
The easiest way to identify broken link issues is to run a site audit using the free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
After creating an account, navigate to Site Audit and click + New Project.
After adding your site, it may take up to a day for Ahrefs to gather and process useful data about your site, though in most cases, this happens much faster.
Once the Site Audit tool has crawled your site, go to Reports – Links, where you’ll see a breakdown of the total number of broken internal and external links on your site.
Clicking on either of those numbers will bring up a full list of broken links and show you what the problem is so that you can set about fixing it.
9. Missing Structured Data
Structured data involves labeling and organizing your website content into a standardized format that search engines can easily understand through the use of markup code.
The Problem:
As Google evolves to prioritize semantic search and knowledge graphs, implementing structured data such as Schema markup to your website will ensure your content is accurately understood and presented, maximizing your ranking potential.
If you’re not using structured data, or you’re not using it effectively, you’re missing out on a chance to vastly improve your search visibility.
The Cause:
The main reason why structured data is missing on many websites is that it’s a concept many novice WordPress users are still unfamiliar with, while those who do know about it may be put off by the need to use code.
If structured data is in place, it can still be ineffective if it isn’t implemented correctly and comprehensively.
The Solution:
The good news is that you don’t have to be a coding whiz to make the most of structured data.
Top WordPress SEO plugins like Rankmath typically include user-friendly interfaces through which you can add schema markup without typing a single line of code.
There’s also a plethora of free and paid plugins like Schema & Structured Data designed specifically to make structured data easier to understand and manage.
Technical SEO Pain Points: Key Takeaway
By now, one thing should be obvious about technical SEO:
It’s all about giving your users the best possible site experience, ensuring pages load quickly and function correctly no matter what device a visitor uses.
When you focus on improving site speeds, mobile-friendliness, and getting your content indexed for relevant keywords, you not only reap the rewards of better engagement and higher conversion rates but also the added bonus of appeasing Google’s search crawlers, meaning higher search rankings, more visitors, and continued success.
Prefer to leave your technical SEO pain points to someone else? Talk to UnlimitedWP today to discover how we can help.